Improving Property Graph Layouts by Leveraging Attribute Similarity for Structurally Equivalent Nodes
Patrick Mackey - Pacific Northwest National Lab, Richland, United States
Jacob Miller - University of Arizona, Tucson, United States. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, United States
Liz Faultersack - Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, United States
Room: Bayshore VI
2024-10-16T12:48:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-16T12:48:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
graph drawing, network visualization, property graphs, attributed networks
Abstract
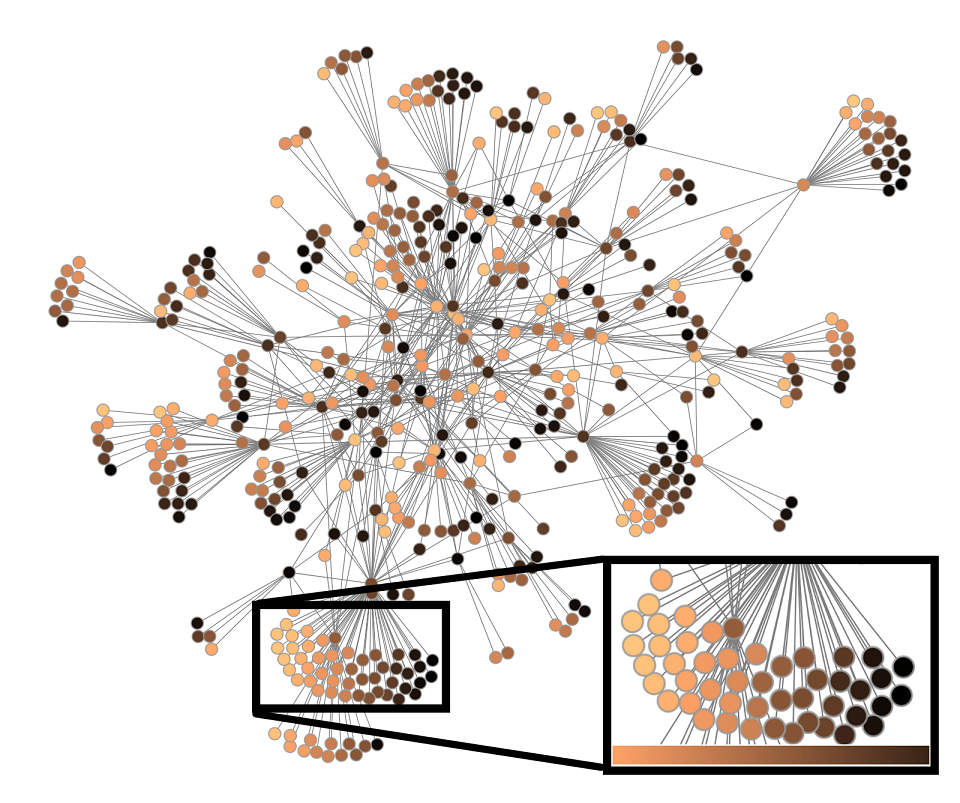
Many real-world networks contain structurally-equivalent nodes. These are defined as vertices that share the same set of neighboring nodes, making them interchangeable with a traditional graph layout approach. However, many real-world graphs also have properties associated with nodes, adding additional meaning to them. We present an approach for swapping locations of structurally-equivalent nodes in graph layout so that those with more similar properties have closer proximity to each other. This improves the usefulness of the visualization from an attribute perspective without negatively impacting the visualization from a structural perspective. We include an algorithm for finding these sets of nodes in linear time, as well as methodologies for ordering nodes based on their attribute similarity, which works for scalar, ordinal, multidimensional, and categorical data.