An Overview + Detail Layout for Visualizing Compound Graphs
Chang Han - University of Utah, Salt Lake City, United States
Justin Lieffers - University of Arizona, Tucson, United States
Clayton Morrison - University of Arizona, Tucson, United States
Katherine E. Isaacs - The University of Utah, Salt Lake City, United States
Download preprint PDF
Room: Bayshore VI
2024-10-16T12:39:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-16T12:39:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
compound graphs, network layout, graph drawing, network visualization, graph visualization
Abstract
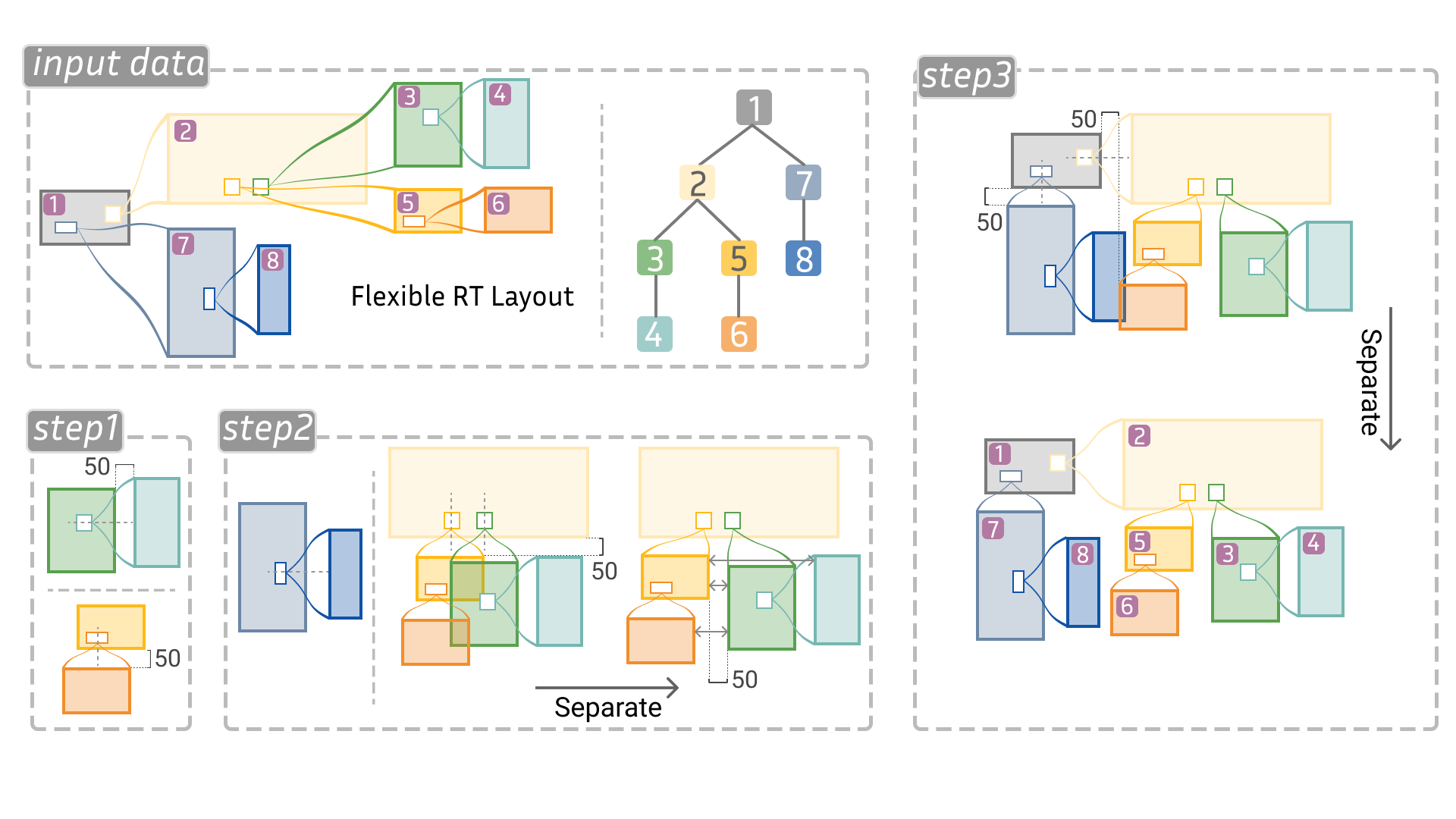
Compound graphs are networks in which vertices can be grouped into larger subsets, with these subsets capable of further grouping, resulting in a nesting that can be many levels deep. In several applications, including biological workflows, chemical equations, and computational data flow analysis, these graphs often exhibit a tree-like nesting structure, where sibling clusters are disjoint. Common compound graph layouts prioritize the lowest level of the grouping, down to the individual ungrouped vertices, which can make the higher level grouped structures more difficult to discern, especially in deeply nested networks. Leveraging the additional structure of the tree-like nesting, we contribute an overview+detail layout for this class of compound graphs that preserves the saliency of the higher level network structure when groups are expanded to show internal nested structure. Our layout draws inner structures adjacent to their parents, using a modified tree layout to place substructures. We describe our algorithm and then present case studies demonstrating the layout's utility to a domain expert working on data flow analysis. Finally, we discuss network parameters and analysis situations in which our layout is well suited.