Extreme Weather and the Power Grid: A Case Study of Winter Storm Uri
Baldwin Nsonga - Institute of Computer Science, Leipzig University, Leipzig, Germany
Andy S Berres - National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, United States
Robert Jeffers - National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, United States
Caitlyn Clark - National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, United States
Hans Hagen - University of Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany
Gerik Scheuermann - Leipzig University, Leipzig, Germany
Room: Bayshore VI
2024-10-14T16:00:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-14T16:00:00Z
Fast forward
Abstract
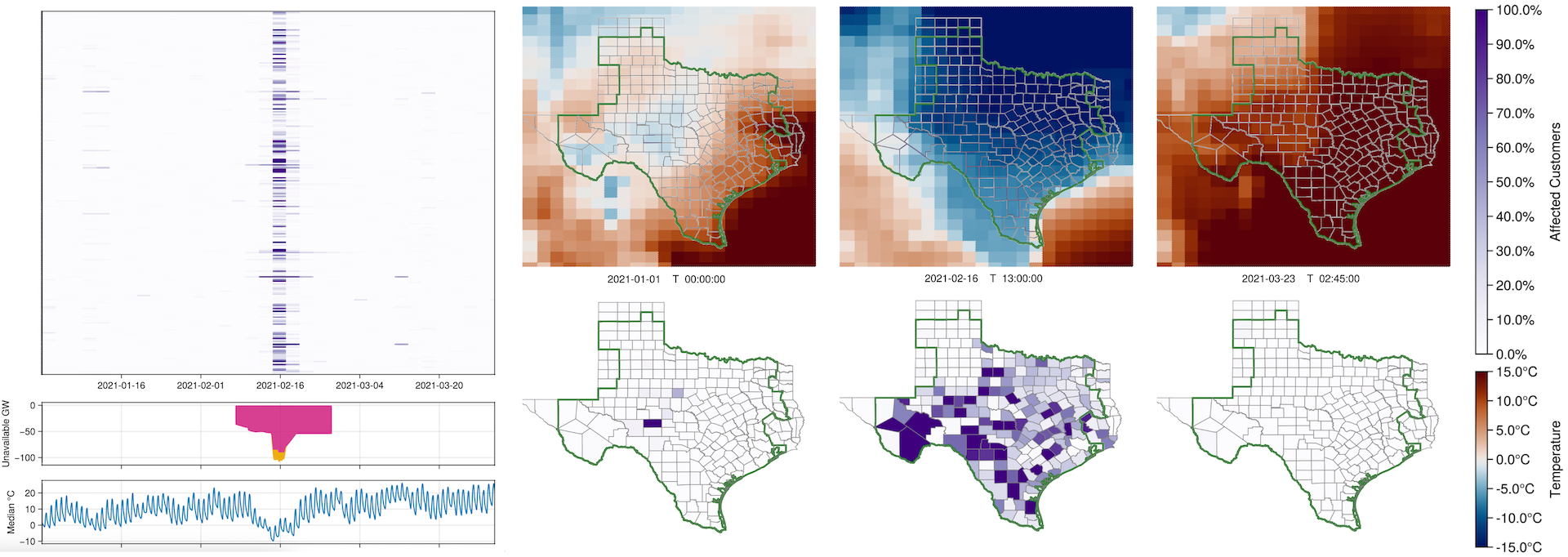
Weather can have a significant impact on the power grid. Heat and cold waves lead to increased energy use as customers cool or heat their space, while simultaneously hampering energy production as the environment deviates from ideal operating conditions. Extreme heat has previously melted power cables, while extreme cold can cause vital parts of the energy infrastructure to freeze. Utilities have reserves to compensate for the additional energy use, but in extreme cases which fall outside the forecast energy demand, the impact on the power grid can be severe. In this paper, we present an interactive tool to explore the relationship between weather and power outages. We demonstrate its use with the example of the impact of Winter Storm Uri on Texas in February 2021.