Challenges in Data Integration, Monitoring, and Exploration of Methane Emissions: The Role of Data Analysis and Visualization
Parisa Masnadi Khiabani - University of Oklahoma, Norman, United States
Gopichandh Danala - University of Oklahoma, Norman, United States
Wolfgang Jentner - University of Oklahoma, Norman, United States
David Ebert - University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma, United States
Room: Bayshore VI
2024-10-14T16:00:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-14T16:00:00Z
Abstract
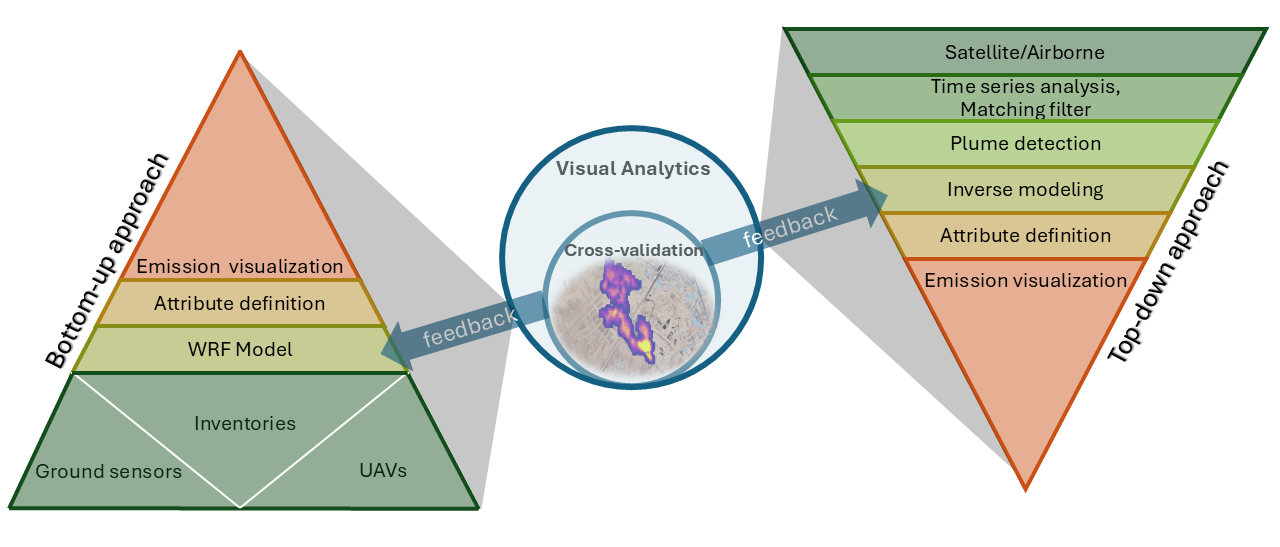
Methane (CH4) leakage monitoring is crucial for environmental protection and regulatory compliance, particularly in the oil and gas industries. Reducing CH4 emissions helps advance green energy by converting it into a valuable energy source through innovative capture technologies. A real-time continuous monitoring system (CMS) is necessary to detect fugitive and intermittent emissions and provide actionable insights. Integrating spatiotemporal data from satellites, airborne sensors, and ground sensors with inventory data and the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model creates a comprehensive dataset, making CMS feasible but posing significant challenges. These challenges include data alignment and fusion, managing heterogeneity, handling missing values, ensuring resolution integrity, and maintaining geometric and radiometric accuracy. This study outlines the procedure for methane leakage detection, addressing challenges at each step and offering solutions through machine learning and data analysis. It further details how visual analytics can be implemented to improve the effectiveness of the various aspects of emission monitoring.