Critical Point Extraction from Multivariate Functional Approximation
Guanqun Ma - University of Utah, Salt Lake City, United States
David Lenz - Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, United States
Tom Peterka - Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, United States
Hanqi Guo - The Ohio State University, Columbus, United States
Bei Wang - University of Utah, Salt Lake City, United States
Screen-reader Accessible PDF
Download preprint PDF
Room: Bayshore III
2024-10-14T16:00:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-14T16:00:00Z
Fast forward
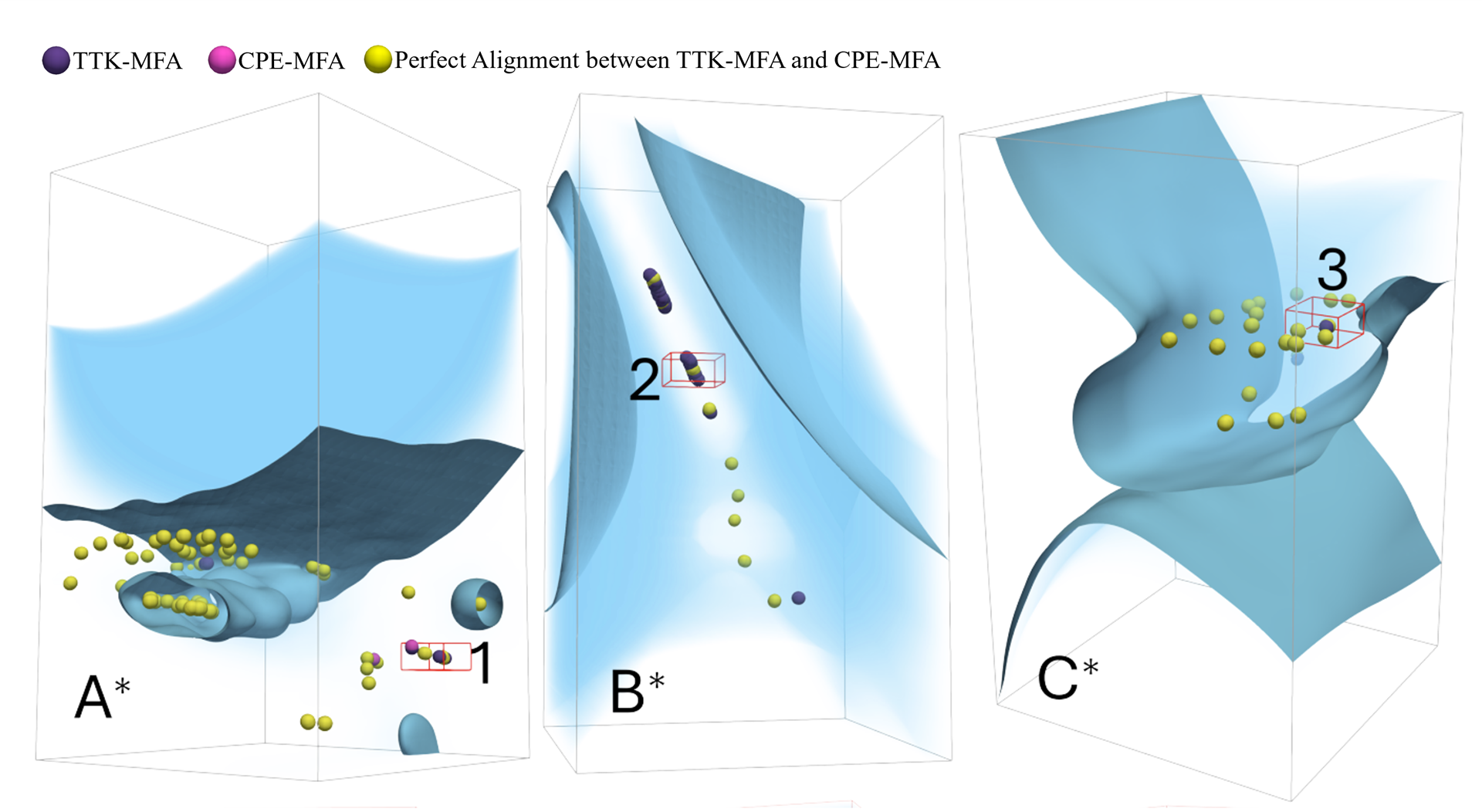
Abstract
Advances in high-performance computing require new ways to represent large-scale scientific data to support data storage, data transfers, and data analysis within scientific workflows. Multivariate functional approximation (MFA) has recently emerged as a new continuous meshless representation that approximates raw discrete data with a set of piecewise smooth functions. An MFA model of data thus offers a compact representation and supports high-order evaluation of values and derivatives anywhere in the domain. In this paper, we present CPE-MFA, the first critical point extraction framework designed for MFA models of large-scale, high-dimensional data. CPE-MFA extracts critical points directly from an MFA model without the need for discretization or resampling. This is the first step toward enabling continuous implicit models such as MFA to support topological data analysis at scale.